Glossary Of Terms – Windows and Doors
Window & Door Glossary
We believe educating our customers is essential for a positive experience. At MacFarlane Windows and Doors, we ensure our clients are well-informed about the products they purchase, helping them feel confident in their choices. Whether you’re buying windows or doors, we’re here to make the process simple and stress-free.
Our goal is to ensure you feel comfortable with your purchase decision. Here’s a comprehensive glossary to help you understand the terms commonly used in the industry.
Performance Metrics
- Air Infiltration: Measures air seeping through a window or door. Measured in CFM (cubic feet per minute) or LPS (liters per second).
- Condensation: Water deposition on cool surfaces when warm, moisture-heavy air contacts them.
- ENERGY STAR®: A government program that helps consumers identify energy-efficient products.
- R-value: Measures thermal resistance; higher values mean better insulation.
- U-factor: Indicates heat transfer; lower values mean better insulation.
- Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC): Measures how much solar heat passes through a window.
- Sound Transmission Class (STC): Rates how well a window or door blocks sound.
- Visible Transmittance (VT): Measures how much visible light passes through a window.
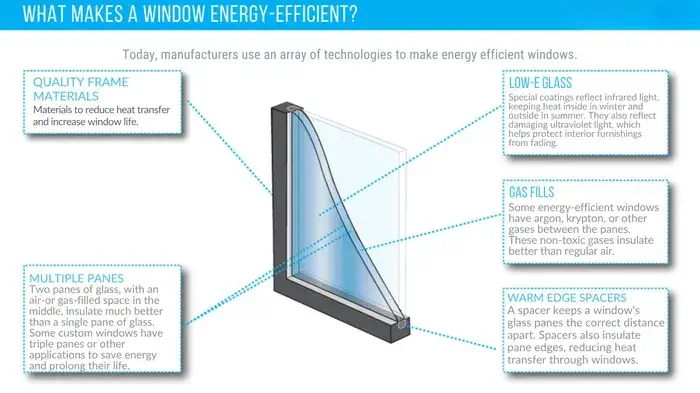
Glass Options
- Argon Gas: Used between panes to enhance insulation.
- Krypton Gas: Offers even better insulation properties than argon gas.
- Low-E Glass: Coated glass to reduce heat loss.
- Double-Pane Glass: Two panes of glass with an air gap for insulation.
- Triple-Pane Glass: Three panes of glass for enhanced insulation.
- Tempered Glass: Shatters into small pieces for safety.
- Laminated Glass: Does not shatter when broken, enhancing safety and noise reduction.
- Impact Glass: Designed to withstand high winds and flying debris.
- Obscure Glass: Textured or patterned glass for privacy.
Window Styles
- Awning Window: Hinged at the top and swings outward; great for ventilation even in light rain.
- Bay Window: Three or more panels projecting outward, often with a central fixed pane.
- Bow Window: Similar to a bay window but with a gentler curve.
- Casement Window: Hinged on one side and swings outward.
- Clerestory Window: Installed high on a wall for light and ventilation.
- Dormer Window: Protrudes from the roof, common in Cape Cod-style homes.
- Hopper Window: Hinged at the bottom and opens inward, often used in basements.
- Picture Window: A large fixed window ideal for scenic views.
- Slider Window: Opens horizontally along a track.
- Tilt-and-Turn Window: Opens inward from the top for ventilation or the side for cleaning.
Door Features
- Astragal: Fills the gap between double doors for a better seal.
- Escutcheon Plate: Decorative cover around a door handle.
- Fire-Rated Door: Designed to resist fire for a specific period, often used between a home and garage.
- French Door: Glass-paned doors separated by partitions, often opening to patios.
- Multi-Point Lock: Engages at multiple points for enhanced security.
- Pocket Door: Slides into a wall cavity to save space.
- Striker Plate: Metal plate on the doorframe where the latch engages.
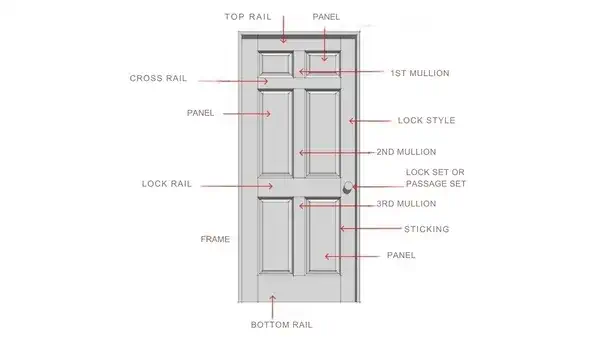
Frame & Installation Terms
- Casing: Trim that covers the edge between the window and wall.
- Cladding: Weather-resistant material on the exterior frame.
- Flashing: Material that prevents water infiltration around windows.
- Brickmould: Exterior trim bridging the gap between the window and siding.
- Rough Opening: The wall opening for installing a window or door.
- Shim: Wedge used to level a window or door during installation.
- Thermal Break: Insulating material between metal components to reduce heat transfer.
- Vapour Barrier: Material to seal windows and prevent moisture.
Glass Design Features
- Art Glass: Decorative glass for embellishment.
- Caming: Metal strips joining decorative glass sections.
- Grille: Inserts mimicking individual panes.
- Snap-In Grilles: Easily removable grilles for cleaning.
Hardware Components
- Balancer: Helps in raising and lowering window sashes.
- Operator: Mechanism for opening and closing a window.
- Jamb Clips: Attach the window or door to the jamb.
- Lift: Handle used to open a window.
- Sash Lock: Secures the sash in place.
- Weep Holes: Drainage holes for water.
Miscellaneous Terms
- Fenestration: Openings in walls for windows or doors.
- OX/XO: Labels for stationary and moving parts of a sliding window.
- Mullion: Structural piece joining two or more windows.
- Mulling: The process of joining multiple windows.
- Daylight Opening: The visible glass area of a window.

By understanding these terms, you’ll feel more confident in choosing the perfect windows and doors for your home. Have questions?

